LABORATORY SERVICES
SCOPE OF ACCREDITATION
This accreditation demonstrates technical competency for a defined scope and the operation of a quality management system.
Enviromental
Gravimetric weighing in accordance with NIOSH 0500 and 0600 for:
- Respirable Dust
- Total Dust
CHEMICAL
Diesel Particular Matter in accordance with NIOSH 5040 for:
- Elemental Carbon (EC)
- Organic Carbon (OC)
- Total Carbon (TC)
Microbiological
Environmental Swabs in accordance with SANS 18953 for:
- E-Coli
- Total Aerobic Count
- Yeast and Mould
Gravimetric weighing facility
(SANAS Accredited)
DIESEL PARTICULATE MATTER
SANAS Accredited
Environmental Swab Sampling
SANAS Accredited
Water Quality Sampling and Analysis
Supply of sampling media and external analysis
GRAVIMETRIC
WEIGHING FACILITY
A Gravimetric weighing facility refers to a controlled environment where the mass of airborne contaminants, typically dust or particulate matter, is measured using a calibrated balance scale with high precision. In general, a gravimetric weighing facility is designed to:

Weigh Sampling Filters:
Control Environmental Factors:
Precision Equipment:
Compliance with Standards:
Quality Assurance:
DIESEL PARTICULATE MATTER (SANAS ACCREDITED)
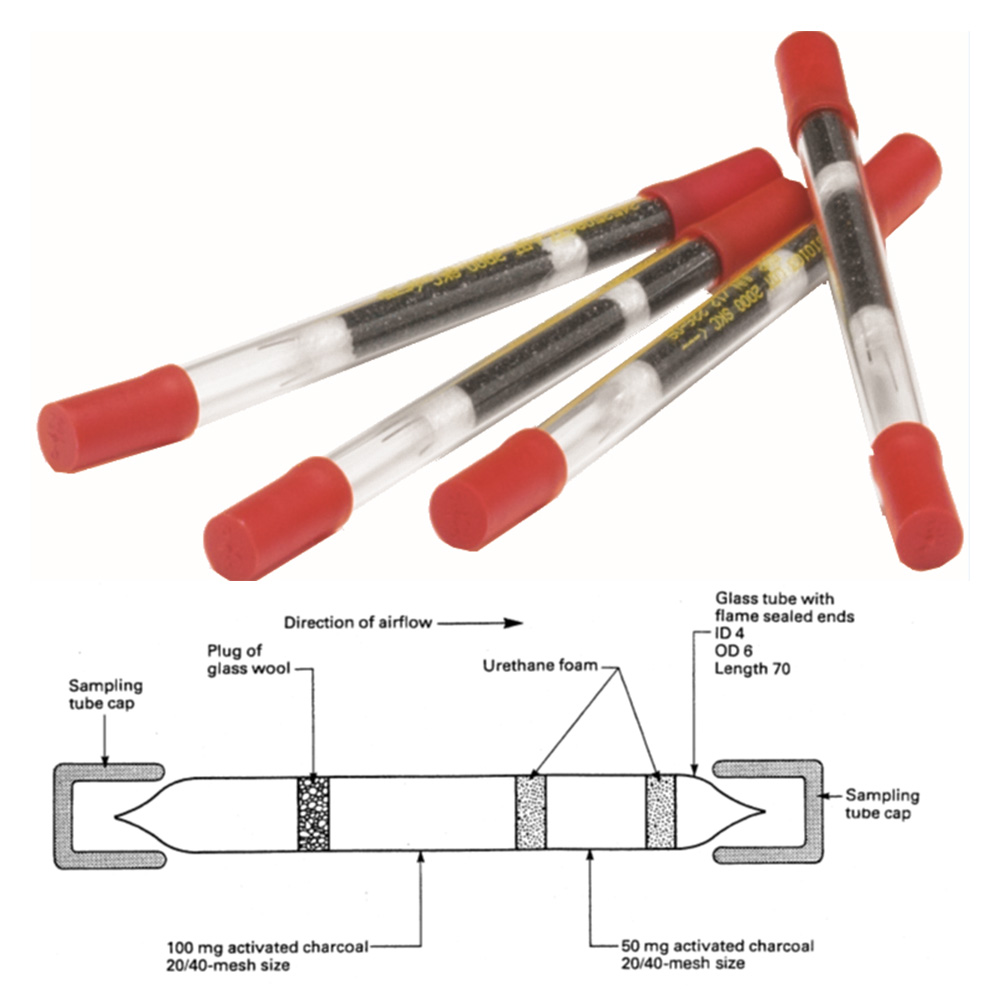
NIOSH Method 5040 is used to analyze diesel particulate matter (DPM) by determining the concentrations of elemental carbon (EC), organic carbon (OC), and total carbon (TC) in air samples. UMOYA makes use of the most recent technology developed by Sunset Laboratories which is an advanced thermal-optical analyzer (TOA), which utilizes a combination of temperature-controlled thermal oxidation and optical detection to precisely separate and quantify EC, OC, and TC from particulate matter collected on sampling filters.
Key steps in the process:
- Elemental Carbon (EC) is determined by heating the sample to high temperatures to burn off the organic material, leaving behind only the elemental carbon.
- Organic Carbon (OC) is measured as the fraction of carbon that is volatilized at lower temperatures.
- Total Carbon (TC) is the sum of EC and OC.
This method is critical for accurately assessing worker exposure to diesel exhaust particles, which contain toxic substances like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and other carcinogens. By differentiating between EC and OC, the method provides a more detailed and accurate measure of DPM, which helps in evaluating the health risks of occupational exposure, setting regulatory limits, and designing effective exposure control measures in industries where diesel engines are common, such as transportation, mining, and construction. This analysis is vital for ensuring workplace safety, compliance with occupational health standards, and ultimately, protecting workers’ respiratory health.
ENVIRONMENTAL SWAB SAMPLING
(SANAS ACCREDITED)
Environmental swab sampling and analysis in accordance with SANS 18953 is a method used to assess the cleanliness of surfaces in the workplace, specifically focusing on the presence of Escherichia coli (EC), aerobic count (AC), and yeast and mould. These microorganisms are indicators of hygiene and cleaning effectiveness in environments where contamination could pose a health risk, such as in food production, healthcare, and other regulated industries.
Swabbing
Analysis
- Escherichia coli (EC), a harmful bacterium often associated with fecal contamination.
- Aerobic count (AC), which measures the total number of aerobic bacteria, indicating overall microbial contamination.
- Yeast and mould, which are fungi that can grow on surfaces and are indicators of poor cleaning, moisture, or spoilage risks

In line with SANS 18953, this sampling and analysis method is vital for evaluating the effectiveness of cleaning protocols in preventing microbial contamination. High levels of EC, AC, or yeast and mould suggest inadequate cleaning and potential risks to worker health, or public safety. Regular environmental swabbing helps ensure that cleaning procedures are effective, maintain compliance with health and safety standards, and reduce the risk of cross-contamination in critical areas, such as food processing or healthcare environments. This process is crucial for risk management, protecting workers, consumers, and maintaining operational integrity.

WATER QUALITY SAMPLING AND ANALYSIS
Water quality testing in accordance with SANS 241 is essential for ensuring that water used in the workplace—whether for drinking, food preparation, or industrial processes—meets safety and quality standards. SANS 241 outlines the microbiological, chemical, and physical criteria for potable water, ensuring that it is free from harmful contaminants that could pose health risks to workers.
Health and Safety:
Regulatory Compliance:
Operational Integrity:
Risk Management:
Testing water quality in accordance with SANS 241 is therefore vital for protecting worker health, ensuring safe production environments, and meeting legal and industry standards for workplace safety.
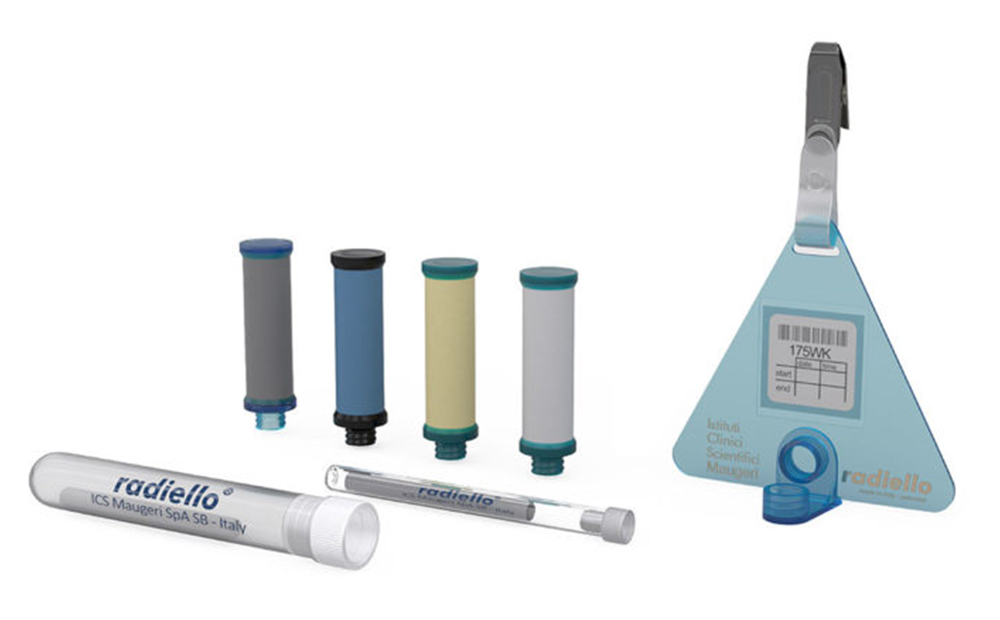
SUPPLY OF SAMPLING MEDIA AND EXTERNAL ACCREDITED ANALYSIS
Occupational hygiene sampling methods and analysis are essential for monitoring and controlling exposure to harmful substances in the workplace, ensuring that workers’ health is protected, and regulatory standards are met.
Personal Air Sampling:
Gases and Vapours:
Asbestos Aerosols:
Dust:
Occupational hygiene sampling helps ensure compliance with workplace safety regulations (e.g., MHSA / OHSA) that set limits for exposure to hazardous chemical substances.